Describe a Polar Covalent Bond Using the Term Electronegativity
Using the Pauling electronegativity bond scale a polar covalent bond has an electronegativity difference between 04 to 17. Use specific examples in your answer.
Of around 03 to 17 When a bond is a polar covalent bond it has an unequal distribution of electrons in the.

. If the difference in electronegativity is greater than 17 the character of the bond will be ionic. A polar bond is a covalent bond in which there is a separation of charge between one end and the other - in other words one end is slightly positive and the other slightly negative. Pure covalent-electrons are being shared equally between atoms.
X A X B 0 then A-B bond is non-polar covalent bond or simply covalent bond and is represented as A-B. A polar bond is a covalent bond in which there is a separation of charge between one end and the other - in other words in which one end is slightly positive and the other slightly negative. Note that this usually only applies to covalent and ionic bonds.
A polar bond is a type of covalent bond in which the electrons forming the bond are unequally distributed. Electronegativity difference between two atoms in a bond can determine what type of bond is used. For more information on Electronegativity Bond Scale.
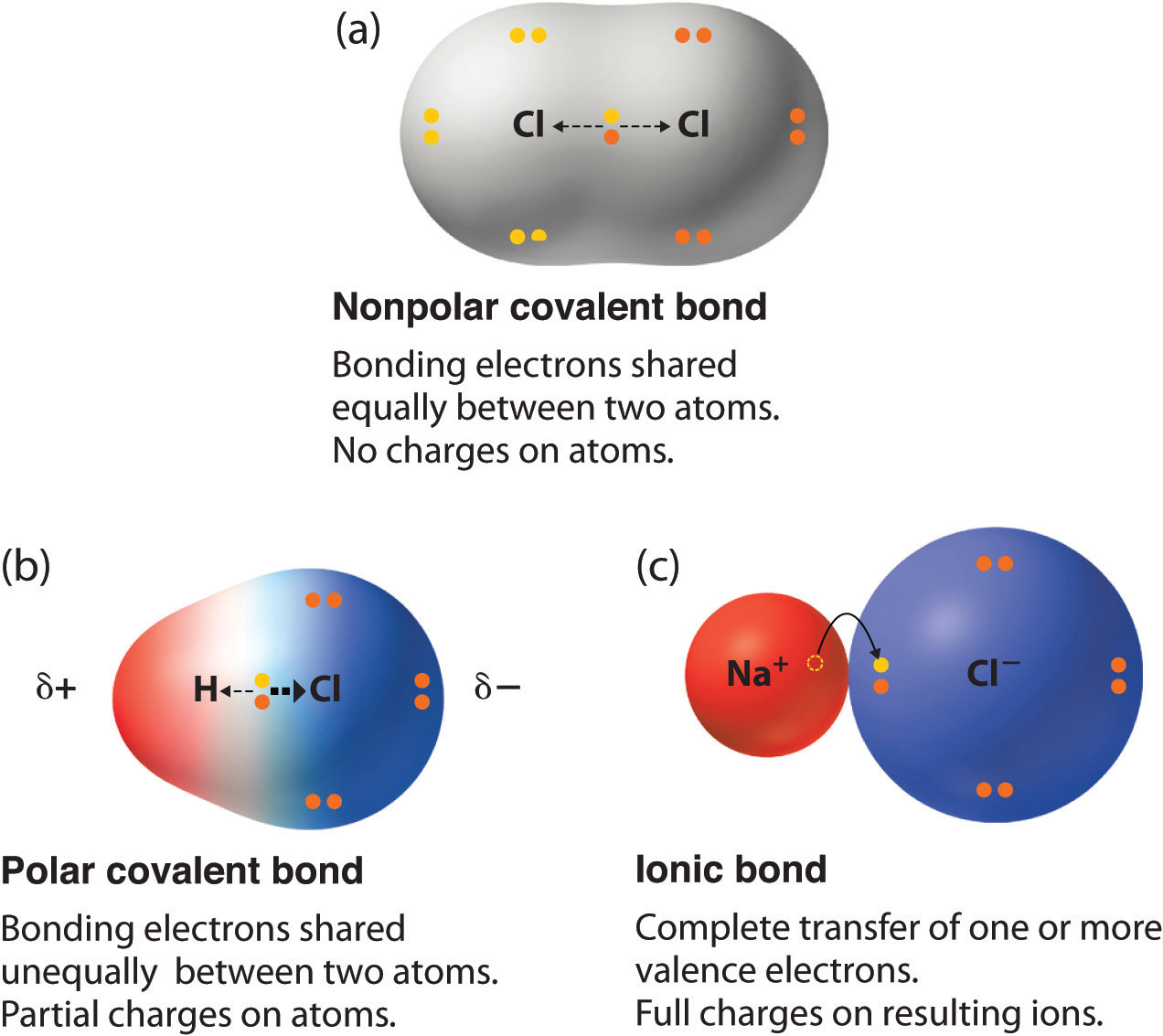
The general rule is that. ΔEN 05the bond is non-polar covalent. In pure covalent bonds the electrons are shared equally.
Ionic Bond Electrovalent Bond Definition Properties Electronegativity Examples With Videos The electrostatic force of attraction between cations and anions are called ionic bond. This property is roughly described as electronegativity If two atoms of differing electronegativity form a bond the electrons spend more time on the more electronegative atom. If their electronegativity values are very different the bond will be ionic because the bonding pair of electrons will mostly be associated with one atom and not the other.
Terms in this set 64 Match each type of bond to the disposition of valence electrons between atoms. Explanation of Polar Covalent Bond. The hydrogen-chlorine bond in HCl or the hydrogen-oxygen bonds in water are typical.
A covalent bond with an unequal sharing of electrons and the electronegativity difference within the range of 01-2 is called a polar covalent bond. The degree to which an atom attracts electrons in a chemical bond is described by electronegativity. QUESTION 3 H-I bond is polar covalent bond.
Electronegativity greater than 4 but less than 2 ex C is 255 and B is 204 a difference of 45 thus a ploar covalent bond. Non-polar polar Electronegativity ENintrinsic ability of an atom to attract the shared electrons in a covalent bondattract the shared electrons in a covalent bond. ΔEN 2the bond is ionic.
Let us consider A and B in which them is. Saturated O supersaturated O undersaturated O unsaturated. Compare nonpolar and polar covalent bonds based on partial change Describe polar covalent bonds of water based on the partial charges of the atoms Describe electronegativity using the definition of Linus Pauling Use electronegativity to distinguish between a polar covalent bond and a non-polar covalent bond Use electronegativity to.
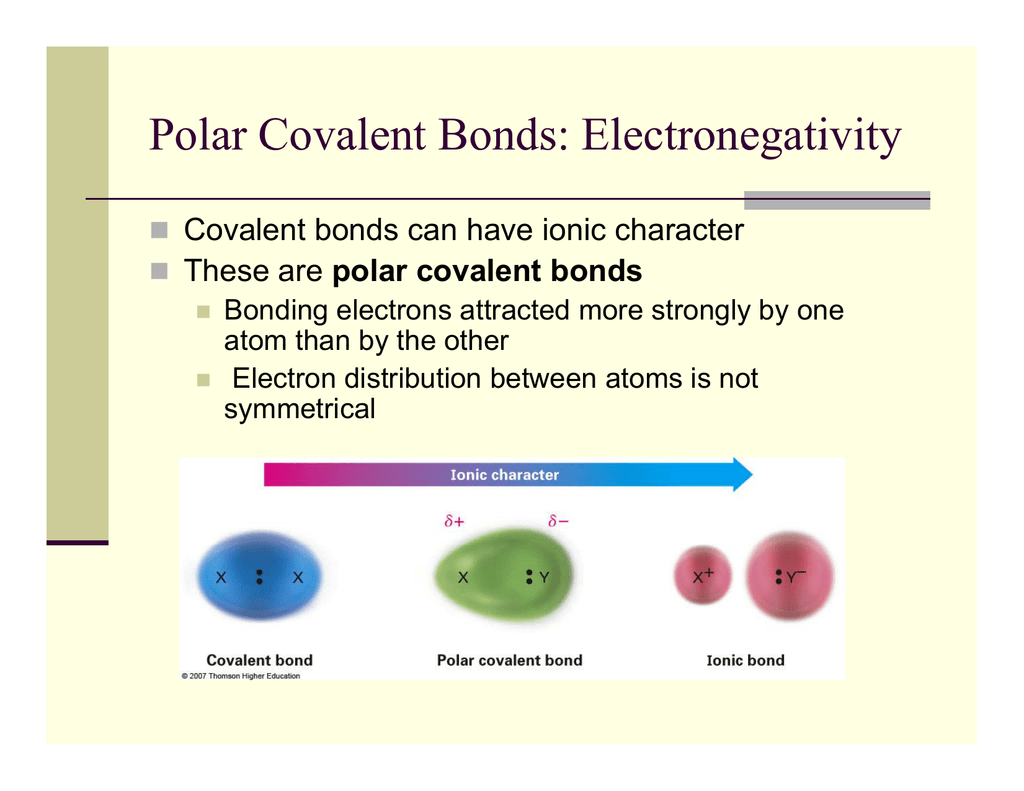
The concept of electronegativity can be used to predict whether the bond between similar or dissimilar atoms is the non-polar covalent bond polar covalent bond or ionic bond. Polar covalent-electrons are being shared unequally between atoms. Polar covalent bonds are usually formed between two nonmetal atoms having different electronegativities.
Use electronegativity to classify bonds as polar covalent pure covalent or ionicTopics. If the difference in electronegativity is between 04 and 17 the character of the bond is polar covalent. The hydrogen fluoride HF molecule has a polar bond between the atoms.
Applications of electronegativity 1 Nature of bond. Polar Covalent is the name used to describe bonds that have both ionic and covalent character because the electrons are shared unequally. So lets review the rules.
Dipole moments are generally found in Polar Covalent Bonds. 05 ΔEN 2the bond is polar covalent. Ex K is 82 and Br is 296 a difference of 214 so ionic bond between the 2.
What is the electronegativity difference for determining a polar covalent bond. C O -. Inductive Effectshifting of sigma bonded electrons in resppygonse to nearby electronegative atom.
Electronegativity determines how the shared electrons are distributed between the two atoms in a polar covalent bond. They form when the electronegativity difference between the anion and cation is between 04 and 17. Some elements tend to attract electrons more strongly than others.
Polar covalent pure covalent electronegati. The ability of an atom to attract a pair of electrons in a chemical bond is called its electronegativity. A covalent bond with an equal share of electrons and an electronegativity difference of zero is called a nonpolar covalent bond.
H-H bond in H. The absolute values of the electronegativity differences between the atoms in the bonds HH HCl and NaCl are 0 nonpolar 09. O True O False QUESTION 4 Which term.
Electronegativity 04 17 Covalent with ionic character polar covalent d d Formation of a permanent dipole polar covalent bond A polar covalent bond forms when the elements in the bond have different electronegativities. Examples include most covalent bonds like the hydrogen-chlorine bond in. In the extreme we have an ionic bond.
The water H 2O molecule has polar bonds. Polar bonds are intermediate between pure covalent bonds and ionic bonds. I When X A X B ie.
Examples include most covalent bonds. Electronegativity Polar Covalent Bonds. What is ionic bond in your own words.
In polar covalent bonds the electrons are shared unequally as one atom exerts a stronger force of attraction on the electrons than the other. If the electronegativity difference usually called ΔEN is less than 05 then the bond is nonpolar covalent. O True O False QUESTION 4 Which term is used to describe a solution that contains less solute than the maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved.
The covalent bond formed between two atoms in molecules whose electronegative difference exists is known as a polar covalent bond. It has no units simple it is a tendency. Electronegativity Bond Scale.
QUESTION 3 H-I bond is polar covalent bond. If the ΔEN is greater than 20 then the bond is ionic. A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms.
Ionic-electrons have been transferred from one atom to another. Elctronegativity greater than 2. The rule is that when the electronegativity difference is greater than 20 the bond is considered ionic.
In other words the electrons spend more time on one side of the bond than the other. Examples of polar covalent bonds. If the ΔEN is between 05 and 16 the bond is considered polar covalent 3.
Polar Covalent Bonds Electronegativity

No comments for "Describe a Polar Covalent Bond Using the Term Electronegativity"
Post a Comment